The Role of Automotive Die Casting in Modern Vehicle Manufacturing
Introduction
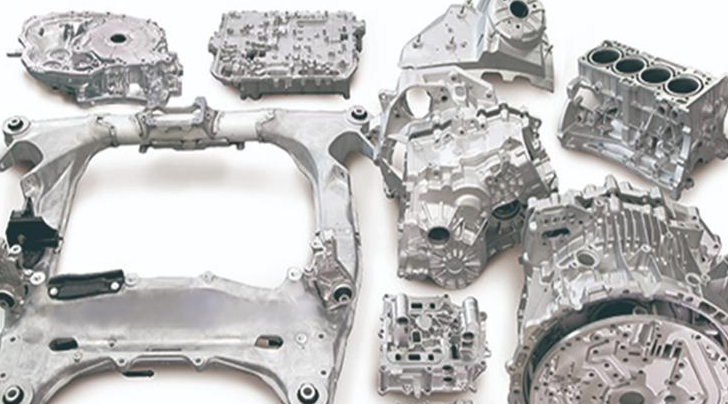
Automotive die casting plays a crucial role in modern vehicle manufacturing, enabling the production of lightweight, durable, and cost-effective components. This process is widely used by automobile manufacturers to produce complex metal parts with high precision. In this article, we will explore the significance of automotive die casting, its benefits, applications, and future trends.
What is Automotive Die Casting?
Die casting is a metal casting process that involves injecting molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. The mold, also known as a die, is typically made from hardened steel and is designed to create precise and intricate metal components. In the automotive industry, die casting is primarily used to manufacture parts made from aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys.
Benefits of Automotive Die Casting
1. Lightweight and High Strength
Die casting allows for the production of lightweight yet strong automotive parts, which helps improve fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
2. Cost-Effective Manufacturing
Mass production of automotive parts using die casting reduces costs associated with labor, materials, and machining. The efficiency of the process minimizes waste and optimizes resource utilization.
3. High Precision and Consistency
Automotive die casting produces highly precise and uniform components, ensuring quality and reliability in vehicle performance. This precision also reduces the need for secondary machining operations.
4. Enhanced Thermal Conductivity
Die-cast aluminum and magnesium components offer excellent heat dissipation properties, which are critical for engine components, transmissions, and electronic housings.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Die-cast metals, especially aluminum and magnesium alloys, exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for automotive applications exposed to harsh environments.
Key Applications of Die Casting in Automotive Manufacturing
1. Engine Components
Die casting is used to produce engine parts such as cylinder heads, engine blocks, and transmission cases, which require high durability and strength.
2. Structural Components
The process is applied to manufacture lightweight structural components like shock towers, cross members, and chassis parts to enhance vehicle stability and safety.
3. Transmission and Drivetrain Parts
Precision die casting helps create gear housings, differential cases, and clutch components that are integral to a vehicle's drivetrain system.
4. Electrical and Electronic Housings
With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), die-cast components are increasingly used for battery enclosures, electronic control unit (ECU) casings, and heat sinks.
5. Braking Systems
Brake calipers and other hydraulic components benefit from die casting due to their need for strength and heat resistance.
Types of Die Casting Processes Used in Automotive Manufacturing
1. High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC)
HPDC is the most commonly used die casting method in the automotive industry. It involves injecting molten metal into a mold under high pressure, resulting in precise and thin-walled components with high strength.
2. Low-Pressure Die Casting (LPDC)
LPDC is used for larger and more complex automotive parts, such as wheels and suspension components. This method provides superior structural integrity and is particularly suitable for aluminum alloys.
3. Gravity Die Casting (GDC)
In this process, molten metal is poured into a mold using gravity. It is used for parts requiring higher ductility and a more refined microstructure, such as engine blocks and cylinder heads.
4. Squeeze Die Casting
Squeeze die casting combines high-pressure die casting with a forging process, resulting in denser and more durable components. It is widely used for critical structural parts in vehicles.
Trends and Innovations in Automotive Die Casting
1. Increased Use of Lightweight Alloys
Automakers are focusing on using lightweight materials such as aluminum and magnesium alloys to enhance fuel efficiency and meet stringent emission standards.
2. Integration of Automation and AI
The use of robotics and artificial intelligence in die casting is improving efficiency, reducing defects, and ensuring consistent quality in automotive parts.
3. 3D Printing for Mold Production
Additive manufacturing (3D printing) is being employed to create complex and highly precise die molds, reducing lead times and improving flexibility in design.
4. Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Practices
Automakers are adopting sustainable die casting processes by recycling metal alloys, reducing energy consumption, and implementing environmentally friendly cooling and lubrication systems.
5. Advancements in Electric Vehicle Components
With the shift towards electric mobility, die-cast components are being optimized for battery packs, power electronics, and lightweight vehicle structures to enhance performance and range.
Challenges in Automotive Die Casting
1. High Initial Tooling Costs
Setting up die casting operations requires significant investment in tooling and machinery, making it a cost-intensive process for new manufacturers.
2. Material Limitations
While aluminum and magnesium offer many benefits, they also have limitations in terms of impact resistance and weldability, requiring innovative solutions for structural applications.
3. Quality Control and Defect Management
Porosity, shrinkage, and cracking are common defects in die casting. Advanced inspection techniques and improved casting methods are essential to maintain quality standards.
4. Market Fluctuations and Supply Chain Issues
The automotive industry faces challenges related to fluctuating raw material prices, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical factors affecting production.
Conclusion
Automotive die casting is a fundamental manufacturing process that has revolutionized vehicle production by providing lightweight, durable, and cost-efficient components. With ongoing advancements in materials, automation, and sustainability, the future of die casting in the automotive sector looks promising. As automakers continue to innovate, die casting will remain a key enabler in the development of next-generation vehicles, including electric and autonomous cars.
FAQs
1. What metals are commonly used in automotive die casting?
Aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys are the most commonly used metals due to their lightweight, durability, and corrosion resistance.
2. Why is die casting important in the automotive industry?
Die casting enables the mass production of high-precision and lightweight components, reducing costs while enhancing vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
3. What are the major challenges in automotive die casting?
Challenges include high tooling costs, quality control issues, material limitations, and supply chain fluctuations.
4. How does die casting contribute to electric vehicle manufacturing?
Die casting plays a crucial role in EV manufacturing by producing lightweight battery enclosures, electronic casings, and heat dissipation components to improve efficiency and performance.
5. What is the future of automotive die casting?
The future of die casting involves increased automation, sustainable practices, 3D printing integration, and advancements in lightweight materials to support next-generation vehicles.
By understanding the role of automotive die casting, manufacturers can optimize production processes, reduce costs, and drive innovation in the automotive sector.
- Questions and Answers
- Opinion
- Motivational and Inspiring Story
- Technology
- Live and Let live
- Focus
- Geopolitics
- Military-Arms/Equipment
- Securitate
- Economy
- Beasts of Nations
- Machine Tools-The “Mother Industry”
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film/Movie
- Fitness
- Food
- Jocuri
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Alte
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Health and Wellness
- News
- Culture

