MRI vs CT Scan of Brain: 10 Key Differences Explained | ER of Coppell

Introduction
When it comes to diagnosing brain-related issues, medical imaging plays a crucial role in uncovering what’s happening inside your head — literally. Many patients wonder about MRI vs CT scan of brain, especially when doctors recommend one over the other. Both technologies create detailed images of the brain, but they work in different ways and serve distinct purposes.
At ER of Coppell, our team uses advanced imaging technology to ensure fast, accurate, and safe diagnosis for patients experiencing neurological symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, trauma, or sudden confusion. Understanding the differences between these two imaging techniques can help you make informed decisions about your care.
What Is an MRI Scan?
MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. It uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of your brain and other organs — without using radiation.
An MRI provides incredibly precise visuals of soft tissues, making it ideal for detecting subtle changes or abnormalities that might not appear on other scans.
How MRI Works
-
The patient lies inside a large cylindrical machine.
-
Magnetic fields realign hydrogen atoms in the body.
-
Radio waves stimulate these atoms, producing signals.
-
The machine’s computer translates signals into detailed cross-sectional images.
Key Features of MRI
-
No radiation exposure
-
Highly detailed soft tissue imaging
-
Longer scan time (20–60 minutes)
-
Loud machine sounds; may require ear protection
-
Safe for most patients, but not for those with metal implants or pacemakers
What Is a CT Scan?
CT stands for Computed Tomography. It uses X-rays and computer technology to create images of your brain from multiple angles. CT scans are especially effective for identifying bleeding, fractures, and other acute injuries.
At ER of Coppell, CT scans are often used in emergencies because they deliver quick, accurate results — typically within minutes.
How CT Scan Works
-
You lie on a narrow table that moves through a circular scanner.
-
The scanner rotates around your head, taking X-ray images.
-
A computer compiles these images into detailed cross-sections of the brain.
Key Features of CT Scan
-
Uses low-dose radiation
-
Takes only 5–10 minutes
-
Ideal for emergencies
-
Excellent for detecting bone fractures and bleeding
-
May use contrast dye for clearer images
MRI vs CT Scan of Brain: Key Differences
Let’s break down the main distinctions between MRI and CT scans, especially for brain imaging.
| Feature | MRI Scan | CT Scan |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Used | Magnetic fields and radio waves | X-rays |
| Radiation Exposure | None | Yes (low-dose) |
| Best For | Soft tissue and brain detail | Bone, bleeding, and trauma |
| Image Quality | High resolution, detailed | Quick overview, less detail |
| Time Taken | 20–60 minutes | 5–10 minutes |
| Contrast Used | Gadolinium-based | Iodine-based |
| Suitability for Emergencies | Slower, detailed diagnosis | Faster, immediate emergencies |
| Claustrophobia Risk | Higher | Low |
| Availability | May require scheduling | Widely available |
| Cost | Higher | More affordable |
When Doctors Recommend MRI vs CT Scan of Brain
Doctors choose between MRI and CT based on symptoms, urgency, and what needs to be diagnosed.
Here’s a simple way to understand when each is preferred.
When an MRI Is Recommended
-
Persistent or severe headaches
-
Brain tumors or cancer screening
-
Multiple sclerosis (MS) or demyelination
-
Stroke follow-up (after stabilization)
-
Detailed look at brain tissues, nerves, or vessels
-
Developmental brain disorders in children
When a CT Scan Is Recommended
-
Head injuries or skull fractures
-
Suspected brain bleeding or hemorrhage
-
Stroke diagnosis (acute phase)
-
Brain swelling after trauma
-
Emergency situations needing quick results
-
Detection of bone or sinus abnormalities
At ER of Coppell, physicians evaluate your condition carefully to decide which imaging scan is the safest and most effective option.
Advantages of MRI for Brain Imaging
MRI technology provides unparalleled precision when examining soft tissues, nerves, and blood vessels.
Key Benefits:
-
Exceptional Soft Tissue Detail: Detects minute abnormalities in the brain structure.
-
No Radiation: Safe for repeated use.
-
Superior for Neurological Conditions: Ideal for detecting brain tumors, lesions, and infections.
-
Multiplanar Imaging: Captures the brain from multiple angles for deeper insight.
-
Functional MRI (fMRI): Shows brain activity and blood flow during specific tasks.
Limitations:
-
Longer duration — not ideal in emergencies.
-
May be uncomfortable for claustrophobic patients.
-
Metal implants can interfere with magnetic fields.
Advantages of CT Scan for Brain Imaging
CT scans are often the first imaging choice in trauma or emergency situations due to speed and availability.
Key Benefits:
-
Extremely Fast: Results available in minutes.
-
Excellent for Acute Injuries: Detects bleeding, skull fractures, and swelling instantly.
-
More Accessible: Available in most emergency settings.
-
Painless and Noninvasive: Simple procedure with minimal discomfort.
Limitations:
-
Exposure to low-level radiation.
-
Not as detailed for soft tissues compared to MRI.
-
Contrast dye may cause allergic reactions in rare cases.
Safety Considerations for MRI and CT Scans
Both MRI and CT scans are considered safe when performed by trained professionals. However, there are specific safety points to consider for each.
MRI Safety:
-
Not recommended for patients with metal implants, pacemakers, or metal fragments in the body.
-
Pregnant women should inform their doctor before undergoing MRI.
-
May cause discomfort for patients with claustrophobia.
CT Scan Safety:
-
Involves low-dose radiation exposure, so not ideal for repeated scans.
-
Contrast dyes can sometimes cause allergic reactions or affect kidney function.
-
Not typically recommended during early pregnancy.
At ER of Coppell, patient safety is the top priority. Every imaging procedure is conducted following strict safety protocols and physician oversight.
Which One Is Better for Diagnosing Brain Problems?
Both MRI and CT scans have their strengths — the “better” option depends entirely on what the doctor needs to investigate.
MRI Is Better For:
-
Detecting brain tumors
-
Diagnosing multiple sclerosis (MS)
-
Evaluating long-term brain damage
-
Mapping blood vessels (MRA)
-
Investigating chronic neurological issues
CT Scan Is Better For:
-
Detecting bleeding after a head injury
-
Diagnosing strokes quickly
-
Finding skull fractures or bone injuries
-
Assessing brain swelling or fluid buildup
-
Handling emergencies where time is critical
Summary:
MRI offers deeper, detailed insights, while CT scans provide fast, lifesaving results during emergencies. In many cases, doctors use both together for a complete diagnosis.
What to Expect During Each Procedure
During an MRI:
-
You’ll change into a gown and remove all metal objects.
-
You’ll lie flat on a sliding table that moves into a tunnel-shaped scanner.
-
The machine makes loud tapping or knocking sounds.
-
You must stay still for 20–60 minutes while images are captured.
Tip: If you feel anxious, ER of Coppell staff can provide earplugs or mild relaxation techniques.
During a CT Scan:
-
You’ll lie on a table that slides through a ring-shaped scanner.
-
The machine takes multiple X-ray images in just minutes.
-
You might receive a contrast dye via IV for better visualization.
-
The process is painless and usually finished within 10 minutes.
Tip: Let the team know if you’re allergic to iodine-based dyes before the procedure.
MRI vs CT Scan: Cost Comparison
The cost of these imaging tests can vary depending on the location, facility, and whether contrast dye is used.
| Scan Type | Average Cost Range (USA) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| MRI of Brain | $800 – $2,500 | Detailed but higher cost |
| CT Scan of Brain | $300 – $1,200 | Faster, more affordable |
At ER of Coppell, transparent pricing and insurance support ensure you understand all costs before the procedure.
Choosing the Right Scan at ER of Coppell
At ER of Coppell, board-certified emergency physicians carefully evaluate symptoms, history, and urgency before recommending either scan.
Why Patients Trust ER of Coppell:
-
24/7 emergency and imaging availability
-
On-site MRI and CT scan equipment
-
Rapid diagnosis and results
-
Minimal wait times
-
Compassionate, expert care for adults and children
Your health and safety always come first — and our advanced technology ensures every diagnosis is as precise as possible.
MRI vs CT Scan of Brain in Emergencies
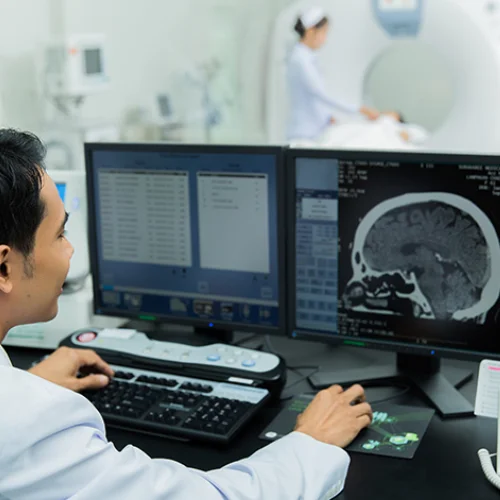
When a patient arrives with sudden neurological symptoms — such as confusion, fainting, or head injury — time becomes critical.
-
CT scans are preferred initially due to their speed and ability to detect bleeding or fractures.
-
MRI may follow later for a more detailed analysis of brain tissue or damage cause.
This two-step approach ensures both accuracy and immediate life-saving action, a standard practice at ER of Coppell.
FAQs About MRI vs CT Scan of Brain
1. Which scan is safer?
MRI is safer since it doesn’t use radiation. However, CT scans are also considered safe when used appropriately, especially in emergencies.
2. Does an MRI show more detail than a CT scan?
Yes. MRI provides higher-resolution images, especially of soft tissue, nerves, and the brain’s internal structures.
3. Is MRI better than CT for stroke detection?
CT is faster for detecting acute strokes (bleeding), but MRI is better for identifying early or small strokes.
4. Can both scans be used together?
Yes. Doctors often use CT first for quick emergency evaluation, then MRI for deeper assessment.
5. Which scan takes longer?
MRI scans take 20–60 minutes, while CT scans take about 5–10 minutes.
6. Are MRI or CT scans painful?
No, both procedures are painless. Some patients may feel slight discomfort from lying still or contrast injection.
7. Can I eat before the scan?
Usually yes, unless your doctor advises fasting (especially if contrast dye is used).
8. Is MRI safe for children?
Yes, MRI is safe and commonly used for children since it doesn’t involve radiation.
Conclusion
Understanding MRI vs CT scan of brain helps you appreciate how modern imaging technology aids in fast, accurate diagnoses.
While MRI provides detailed visuals of the brain’s soft tissues and is excellent for long-term conditions, CT scans are essential for quick decisions during emergencies.
At ER of Coppell, both technologies are available on-site, allowing our physicians to make immediate and informed decisions for every patient — day or night. Whether you’re dealing with sudden head trauma, chronic headaches, or unexplained neurological symptoms, our experienced medical team ensures you receive the best diagnostic care possible.
For More Information Visit
- Questions and Answers
- Opinion
- Motivational and Inspiring Story
- Technology
- Live and Let live
- Focus
- Geopolitics
- Military-Arms/Equipment
- Sicurezza
- Economy
- Beasts of Nations
- Machine Tools-The “Mother Industry”
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film/Movie
- Fitness
- Food
- Giochi
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Altre informazioni
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Health and Wellness
- News
- Culture

